What is O1 interface in ORAN?
The O1 Interface is a logical connection between all “O-RAN Managed Elements (MEs)” and the “management entities” within the SMO framework. The purpose of the O1 interface is to ensure the operation and management e.g. FCAPS, Software Management, and file management of the O-RAN components.
In other words, we can elaborate, the O1 interface enables the management of all O-RAN components that need to be orchestrated and the associated O-RAN network functions. The components managed via O1 include the near-RT RIC, the O-CU, and the O-DU in 5G NR. The O-CU corresponds to a predefined combination of O-CU-CP and O-CU-UP.
The figure below shows an extracted logical O-RAN architecture to illustrate the O1 interface and its influence on O-RAN Manage Elements, including the O-eNodeB. The O-RU termination of the O1 interface towards the SMO is currently under investigation so this interface is shown dashed.
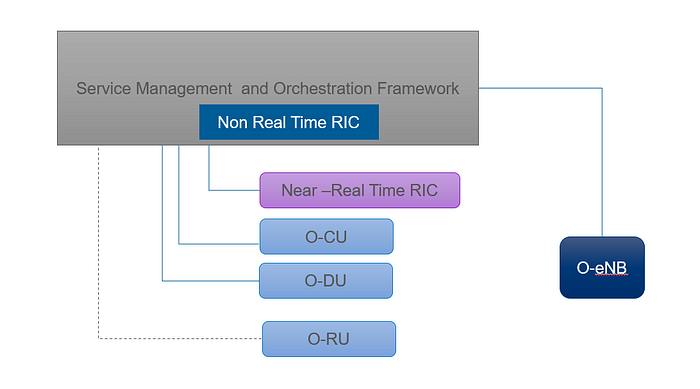
O1 enables the SMO framework to access the O-RAN network functions. Network management is supported in line with the FCAPS model. FCAPS corresponds to the ISO model for network management, which describes and comprises the five functional areas of fault, configuration, accounting, performance and security management. Thus, the O1 interface plays a central role in the overall O-RAN architecture and network operation. O1 supports typical FCAPS and other management functions, including the following functions.
- Discovery/registration
- Configuration of addressing
- Versioning
- Monitoring
O1 Interface Key Pointers
- O1 is the interface between SMO and near-RT RIC, the O-CU, the O-DU, O-RU
- O1 interface ensures the operation and management e.g. FCAPS, Software Management, and file management of O-RAN components
- O1 interface does use standard protocols SSH, TLS, NETCONF
- O1 interface use the Yang Data model
Management Services supported via the O1 Interface
Provisioning management services
- General NETCONF requirements
- Creating, modifying and deleting MOIs (managed object instances)
- Reading MOI attributes
- Notification of changes to MOI attribute values
- Subscription control
Fault supervision management services
- Fault notification
- Fault supervision control
Performance assurance management services
- File reporting and streaming of performance data
- O-RAN-defined performance measurements and control of measurement jobs
Trace Management Services
- Call trace and streaming trace
- Minimization of Drive Testing (MDT)
- Radio Link Failure (RLF) and RRC Connection Establishment Failure (RCEF)
- Trace control
File Management Services
- File readiness notification
- List available files and file download
- Bi-directional transfer of files (e.g. configuration files for beamforming, certificates, ML files) between the client (File Management MnS Consumer) and the file server (File Management MnS Provider)
Communication Surveillance
Heartbeat management services
- Heartbeat notification
- Heartbeat Control
Start-up and registration management services for Physical Network Functions (PNFs)
- PNF plug-and-play
- PNF registration
Software management services for PNFs
- Software package naming and content
- Download, pre-check and activation of software
CNFs an VNFs Life Cycle
- Instantiation and Termination of CNFs/VNFs
- Scaling management services for CNFs/VNFs
The management functionalities are realized by using standard protocols e.g. SSH, TLS, NETCONF and data models e.g. YANG. with the help of the provisioning management service, the SMO framework can receive information (updates) from the MEs via the O1 interface e.g. on the current resource utilization and in return initiate an optimized configuration of the MEs.
In O-RAN-based mobile networks supporting AI/ML approaches, the O1 interface is used to collect (training) data that can be used for ML purposes from the MEs O-DU and O-CU. The (ML-based) non-RT RIC located in the SMO can offer policies to be considered in cell-level optimization by providing (time-varying) optimal configuration sets for cell parameters via the O1 interface.
The O-RAN architecture allows the collection, access to and management of data records (history) relating to the traffic transferred over the RAN, the selected routing and the handover operations carried out. For this purpose, the data is transmitted via the O1 interface.
